Malicious npm Package Impersonates Popular Nodemailer, Puts 3.9M Weekly Downloads at Risk of Crypto Theft
A sophisticated cryptocurrency theft scheme involving a malicious npm package that masquerades as the widely-used Nodemailer email library while secretly hijacking desktop cryptocurrency wallets on Windows systems.
Socket’s Threat Research Team identified the malicious package, nodejs-smtp, which impersonates the legitimate Nodemailer library that averages approximately 3.9 million weekly downloads.
The fraudulent package employs a clever strategy to avoid detection by maintaining full functional compatibility with Nodemailer’s API while executing its malicious payload in the background.
The package presents itself as a legitimate email solution, complete with copied documentation, styling, and README content from the original Nodemailer project.
This careful impersonation allows it to pass casual inspection and enables application tests to continue functioning normally, giving developers little reason to suspect foul play.
Upon installation, the malicious package automatically executes code that specifically targets Atomic Wallet installations on Windows systems. The attack mechanism involves several sophisticated steps:
Wallet Modification Process: The malware uses Electron tooling to unpack Atomic Wallet’s app.asar file, replace a critical vendor bundle with a malicious payload, repackage the application, and remove all traces by deleting its working directory.
Transaction Hijacking: Once embedded within the wallet runtime, the injected code silently overwrites recipient addresses during cryptocurrency transactions, redirecting funds to wallets controlled by the threat actor.
The malware targets multiple cryptocurrencies including Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), Tether (USDT and TRX USDT), XRP, and Solana (SOL).
Persistent Threat Architecture
The modification persists within the wallet’s app.asar file and continues operating across system reboots until the wallet software is completely uninstalled and reinstalled from official sources.
This persistence mechanism ensures continued access to victim transactions even after the original malicious package is removed from the system.
While the financial impact remains limited due to the campaign’s recent launch, security experts warn that the underlying tooling represents a significant threat to the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
The package’s design makes detection particularly challenging for several reasons. Unlike simple typosquatting attacks, nodejs-smtp uses a plausible name that could legitimately appear in search results for “nodejs smtp example” or “simple smtp for nodejs”.
This increases the likelihood that hurried developers might select it without thorough verification.
The risk is further amplified by AI code assistants, which may hallucinate package names that appear appropriate for specific tasks, potentially recommending the malicious package to unsuspecting developers.
This incident exemplifies the growing threat of software supply chain attacks targeting cryptocurrency users.
Recent campaigns have expanded beyond Ethereum and Solana to include TRON and TON cryptocurrencies, with malicious blockchain-related packages continuing to appear across npm and other package ecosystems.
The attack demonstrates how routine developer activities on workstations can quietly compromise separate desktop applications through import-time execution and Electron application manipulation.
Security researchers expect to see more wallet-draining malware delivered through package registries, featuring multichain address mapping and sophisticated modification techniques for desktop applications.
Security Response and Recommendations
At the time of reporting, the malicious nodejs-smtp package remained active on npm, though Socket has petitioned the npm security team for its removal and suspension of the threat actor’s account.
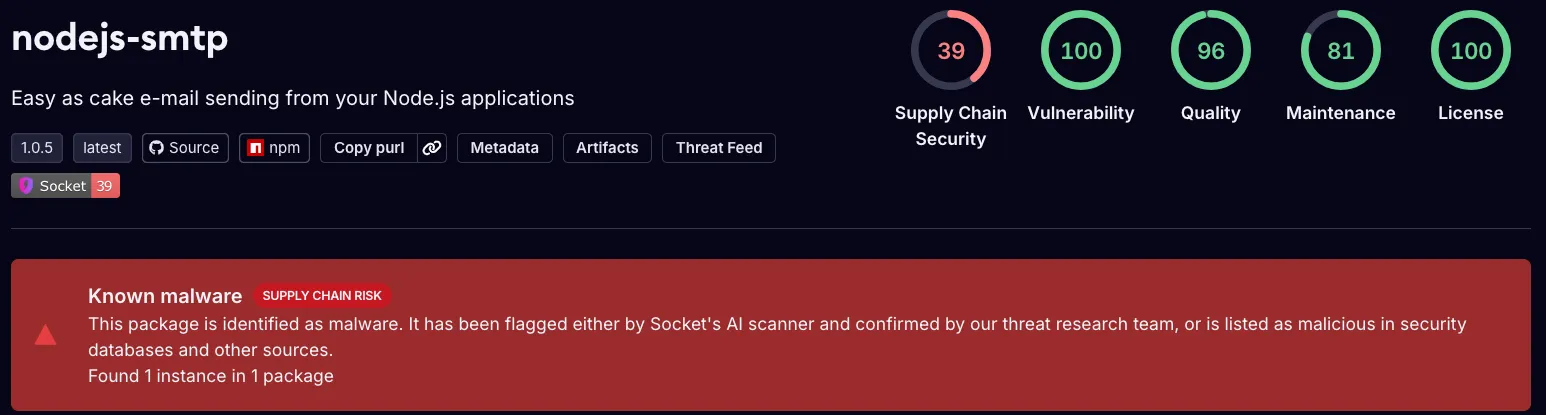
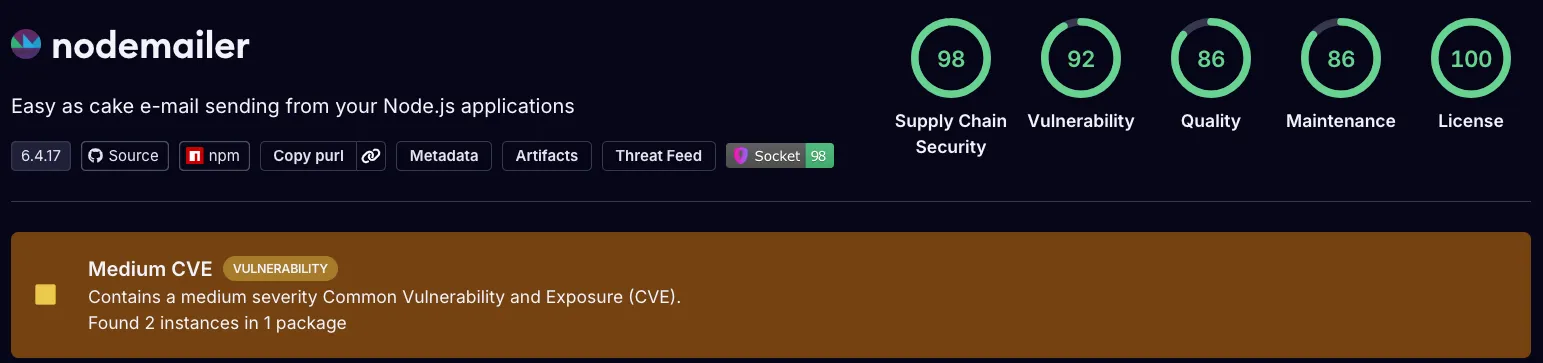
nodejs-smtp (top image) as known malware.The package had accumulated 342 total downloads compared to Nodemailer’s millions of weekly downloads.
Security experts recommend implementing comprehensive supply chain security measures, including real-time package scanning, verification of package authenticity, and monitoring for suspicious install-time behaviors.
Organizations should also consider deploying tools that can detect filesystem manipulation, archive modification, and unexpected vendor bundle modifications during the development process.
The incident underscores the critical importance of vigilant dependency management and the need for enhanced security measures to protect against increasingly sophisticated supply chain attacks targeting the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates.














Post Comment