Hackers Use Hexstrike-AI to Exploit Zero-Day Flaws in Just 10 Minutes
Within hours of its release, the newly unveiled framework Hexstrike-AI has emerged as a game-changer for cybercriminals, enabling them to scan, exploit and persist inside targets in under ten minutes.
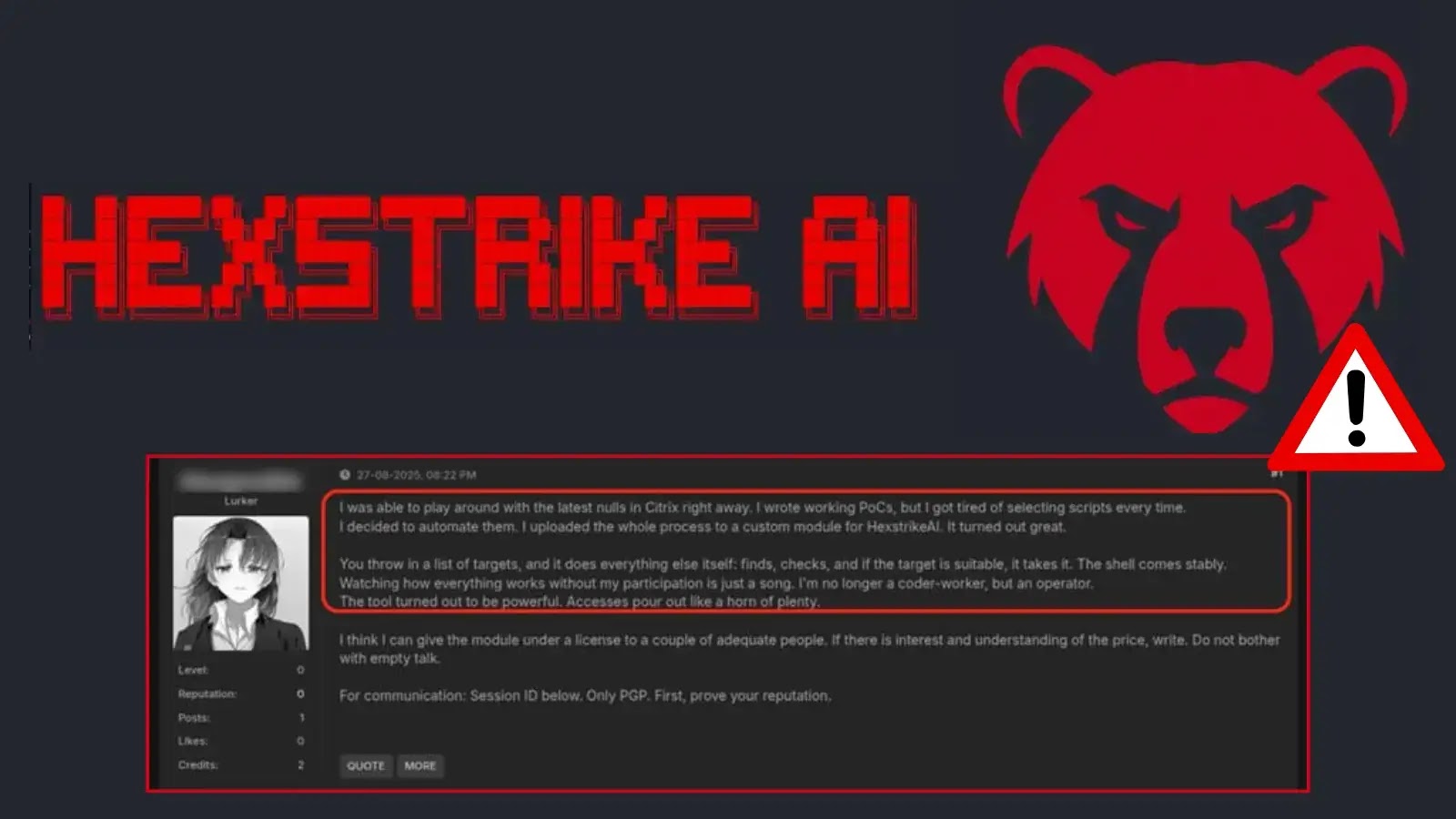
Hexstrike-AI, a red-team tool, quickly turned into a hacking weapon on underground forums, where attackers shared ways to use it against new Citrix NetScaler zero-day flaws.
Security researchers long debated the idea of an AI “brain” to manage many specialized agents working together on complex attacks.
A recent executive blog discussed this idea of orchestration and abstraction layers, predicting it will play a big role in future attacks.

Its creators pitched it to defenders and red teams as “a revolutionary AI-powered offensive security framework,” but malicious actors wasted no time.
By the same afternoon of release, dark-web chatter revealed threat actors testing Hexstrike-AI against Citrix’s newly disclosed NetScaler ADC and Gateway flaws, unleashing unauthenticated remote code execution webshells.
The Architecture of Hexstrike-AI
At its core, Hexstrike-AI features a FastMCP orchestration layer that bridges large language models—such as Claude, GPT and Copilot—with real-world security tooling. Each tool is wrapped in an MCP decorator, exposing it as a callable function.
The system takes unclear commands like “exploit NetScaler” and breaks them into step-by-step actions, letting AI agents carry them out automatically.
- Perform Nmap scans and parse results
- Launch reconnaissance modules across thousands of IPs in parallel
- Execute exploit code and deploy webshells
- Retry failed operations with adaptive variations
Built-in retry logic and resilience loops ensure stability during chained operations, while high-level commands are funneled through an execute_command workflow that dynamically selects and sequences tools.
Weaponizing Critical CVEs
On August 26, Citrix disclosed three critical NetScaler vulnerabilities:
- CVE-2025-7775: Unauthenticated remote code execution
- CVE-2025-7776: Core memory-handling flaw
- CVE-2025-8424: Management interface access control weakness

Historically, exploiting these flaws demanded deep expertise and weeks of development. Yet underground posts now claim successful exploitation and sale of compromised appliances—achieved in a matter of minutes with Hexstrike-AI.
Hexstrike-AI’s release marks a pivotal moment: a defender-oriented tool rapidly repurposed into a large-scale exploitation engine.
The time between disclosure and mass exploitation has shrunk from days to minutes, and attack volumes are poised to surge.
Defenders must act immediately:
- Patch and Harden: Apply Citrix’s fixed builds without delay and restrict NetScaler management interfaces.
- Adopt Adaptive Detection: Move beyond static signatures to AI-driven anomaly detection that learns from ongoing attacks.
- Integrate AI in Defense: Deploy orchestration layers for telemetry correlation and automated response at machine speed.
- Accelerate Patch Cycles: Automate patch validation and deployment to match attackers’ rapid time-to-exploit.
- Monitor Underground Chatter: Fuse dark-web intelligence into threat hunting to gain early warning of emerging tools.
Hexstrike-AI crystallizes the long-predicted convergence of AI orchestration and offensive tooling.
As this operational reality unfolds, the security community must innovate faster—patching smarter, detecting dynamically and responding at machine speed—to stave off the next wave of AI-driven cyberattacks.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates.













Post Comment